Beginner's Guide to Proxy IPs: What is HTTP Proxy?

HTTP proxies, as a common network tool, act as intermediaries between the client and the target server, helping users hide their real IP addresses, bypass geographic restrictions, and improve access speeds. In the following article, let's take a closer look at what HTTP proxies are, how to use them to enhance your online experience, and their practical applications in various scenarios.
I. What is HTTP Proxy?
Before discussing HTTP proxies, let's first clarify two concepts:
1. HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol)
It is an application-layer protocol used for exchanging information on the World Wide Web (Web). It specifies how clients (such as browsers) and servers request and transmit data.
2. Proxy
A proxy is an intermediary service that bridges the gap between the user and the target server. A proxy server receives requests from the client and forwards them to the target server on behalf of the client, then returns the response to the client.
Therefore, an HTTP proxy is a specific type of proxy that is used only for HTTP protocol traffic. It acts as an intermediary between the client and the web server, handling HTTP requests and responses. The HTTP proxy server helps users hide their real IP addresses, improves security, implements access control, caches content, and more by receiving, forwarding, and returning HTTP requests and responses.
II. How Does an HTTP Proxy Work?
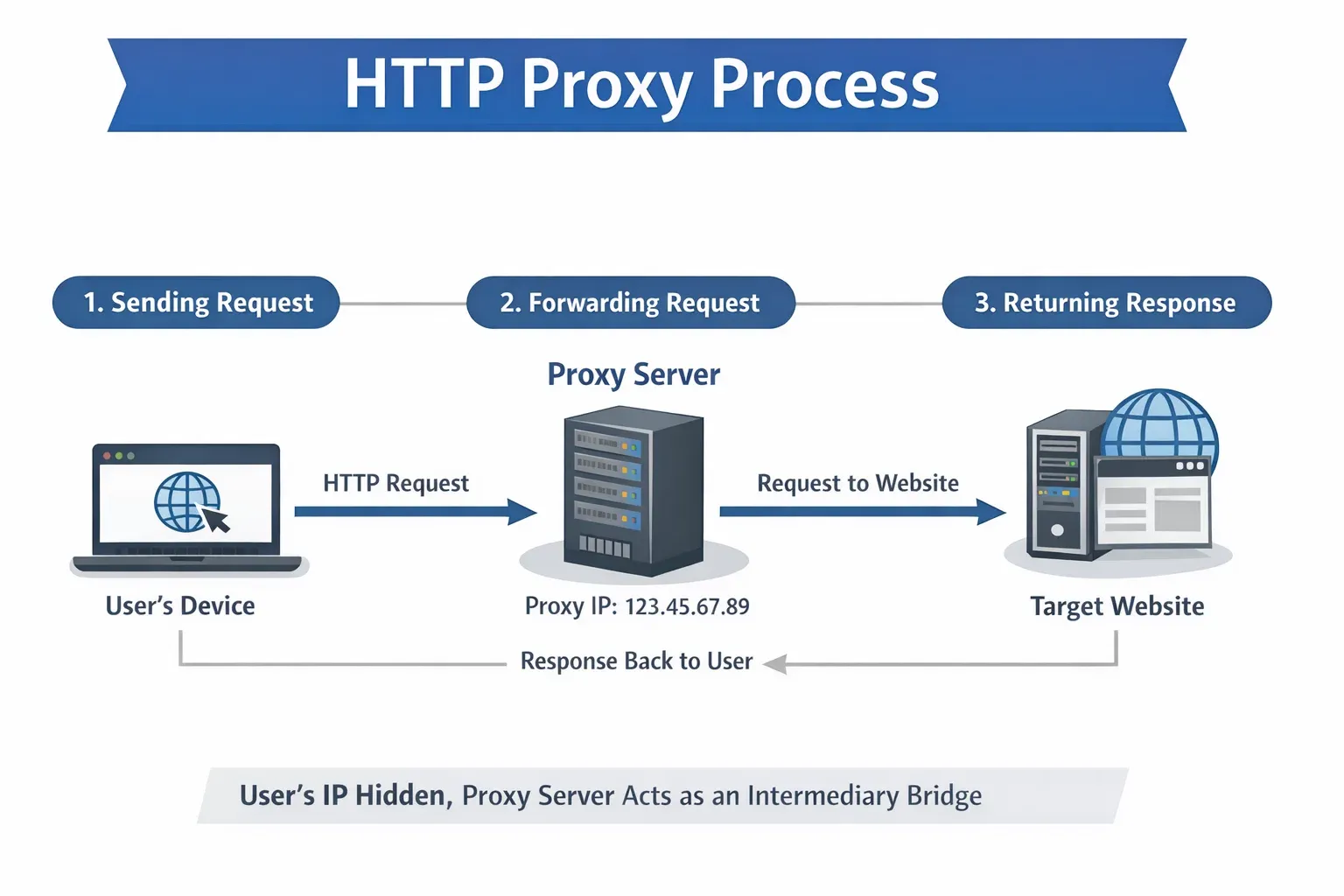
The working principle of an HTTP proxy can be broken down into three basic steps:
1. Sending a Request
The user's device sends an HTTP request via a browser or application to access a website or service. This request first reaches the proxy server, rather than directly going to the target server.
2. Forwarding the Request
Once the proxy server receives the request, it forwards the request to the target website on behalf of the user. At this point, the target website will only see the IP address of the proxy server, not the user's device IP.
3. Returning the Response
The target server sends the requested content back to the proxy server, which then forwards the response data to the user. At this point, the user receives the content from the target website without exposing their real IP address.
III. Advantages of HTTP Proxies
Improved Privacy and Anonymity
By hiding the user's real IP address, the proxy server can effectively prevent the user’s online activities from being tracked.
Bypass Regional Restrictions and Blocks
Many websites or services impose geographic restrictions based on the user’s IP address. If the user's region is restricted from accessing certain content, using an HTTP proxy can bypass this restriction and allow access to the blocked content.
Improved Scraping Efficiency and Security
When performing large-scale data scraping, using an HTTP proxy can effectively prevent the target website from blocking access based on IP. By using a proxy pool, IP rotation can be achieved to avoid being detected as a malicious crawler.
IV. Applications of HTTP Proxies
Cross-border E-commerce
In cross-border e-commerce operations, HTTP proxies can be used to bypass regional restrictions, monitor product pricing, conduct market research, and analyze competitors. By rotating IP addresses, e-commerce platforms can access product information, pricing strategies, and user reviews from other regions, helping to develop more precise marketing strategies.
Web Crawlers and Data Scraping
HTTP proxies play a crucial role in web scraping and data collection. Since target websites often counteract scrapers by blocking IPs or using CAPTCHA, HTTP proxies help avoid IP bans and ensure stable data scraping by using IP rotation techniques.
Ad Verification
Advertising platforms often need to verify ads to ensure they are accurately displayed to the target audience. Using HTTP proxies, different regional IPs can be simulated to verify ad placements and analyze the effectiveness of ad campaigns, helping advertisers optimize their ad content and strategies.
Content Access and Unblocking
For users facing geographic restrictions, HTTP proxies can help them bypass firewalls or regional blocks. For example, in restricted areas, using proxy IPs allows users to access platforms like YouTube or Netflix and enjoy global entertainment content.
V. How to Choose and Use an HTTP Proxy
When selecting an HTTP proxy, consider the following factors:
Proxy Type: Choose the appropriate proxy type based on your needs. Common types include data center proxies and residential proxies. Datacenter proxies are faster, lower-cost, but easier to detect, while residential proxies are more authentic, harder to block, but more expensive.
IP Pool and Rotation: For large-scale data scraping, the quality of the proxy IP pool and the IP rotation mechanism is crucial. Choose a provider that offers IP rotation services to ensure the scraping task runs smoothly.
Security and Anonymity: Ensure the proxy provider guarantees user anonymity and security to prevent data leaks.
Access Speed and Stability: Choose a provider offering fast and stable connections to ensure network access efficiency, especially in cross-border e-commerce and data scraping scenarios.
Price and Service: Choose a provider with a high cost-performance ratio, considering the long-term costs and service quality.
Conclusion
HTTP proxies, as powerful network tools, have widespread applications in privacy protection, network security, cross-border e-commerce, and data scraping. By understanding their working principles and advantages, users can leverage them to enhance their online experience, protect personal privacy, and optimize network connections. Whether it's for ad verification, accessing restricted content, or data scraping, HTTP proxies offer additional convenience and security for users.
FAQs
1. How can I avoid being blocked by the target website when using a proxy?
By using IP rotation, proxy pools, and simulating different regional IPs, you can effectively avoid being detected as a malicious crawler and blocked by the target website.
2. What is the difference between an HTTP proxy and a SOCKS proxy?
HTTP proxies support only HTTP and HTTPS traffic, making them suitable for web browsing. SOCKS proxies, on the other hand, support a wider range of protocols, including FTP, P2P, and others, allowing them to handle more types of traffic.







